ICP-QQQ with oxygen reaction mode for accurate trace-level arsenic analysis in complex samples



Ed McCurdy and Glenn Woods
Agilent Technologies (UK) Ltd.
Keywords
arsenic, zirconium, doubly-charged ion interferences, oxygen mass-shift
Introduction
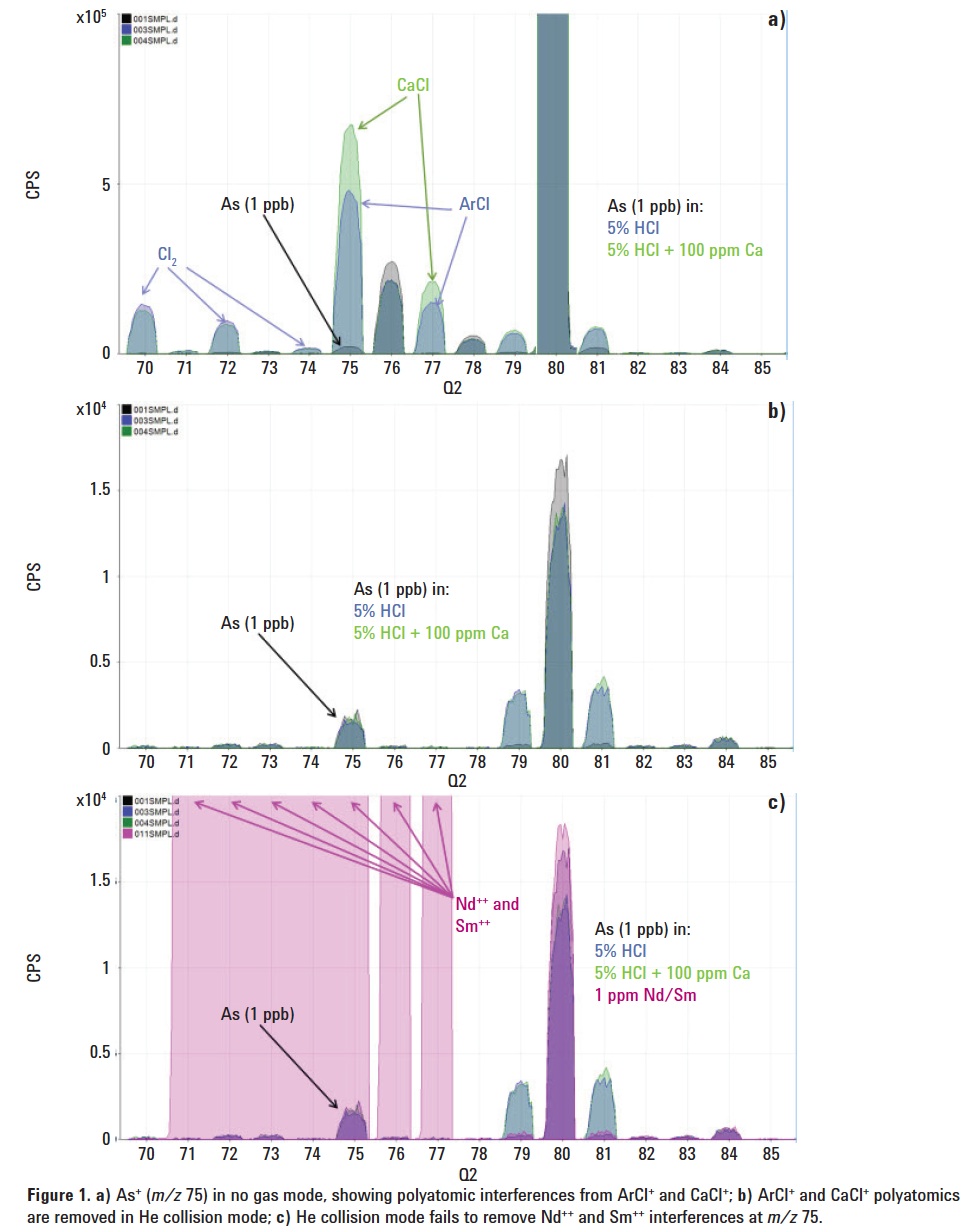
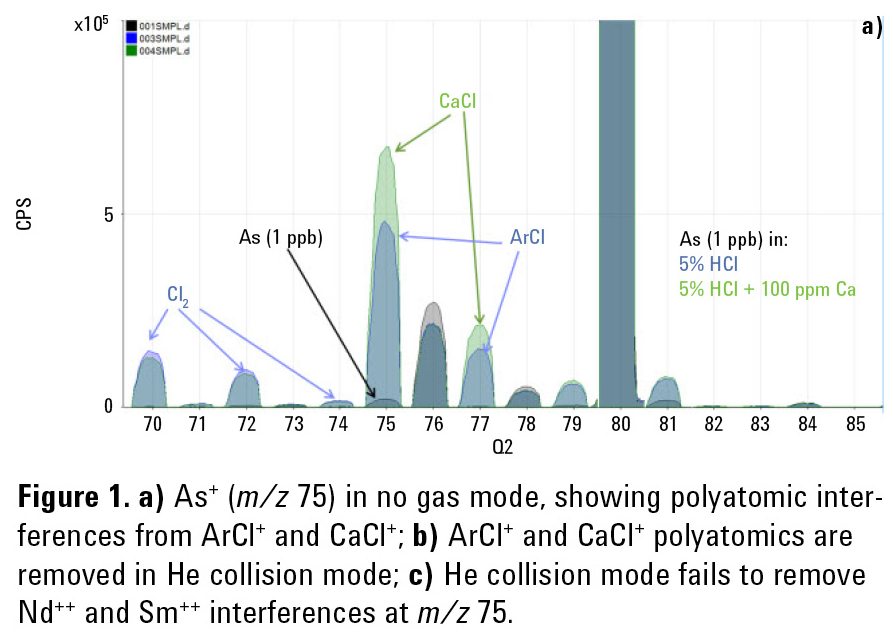
Arsenic (As), with its high first ionization potential and single isotope at mass 75, is one of the most difficult elements to measure accurately by ICP-MS, particularly in complex matrices. The polyatomic interferences from ArCl+ and CaCl+ that overlap As+ at mass 75 can be removed effectively using quadrupole ICP-MS (ICP-QMS) in helium collision mode, but collision mode cannot resolve the doubly-charged ion interferences from 150Nd++and 150Sm++. A quadrupole mass spectrometer separates ions based on their mass to charge ratio (m/z), so doubly-charged ions appear at half their true mass; 150Nd++ and 150Sm++ therefore give an apparent overlap on As at mass 75.
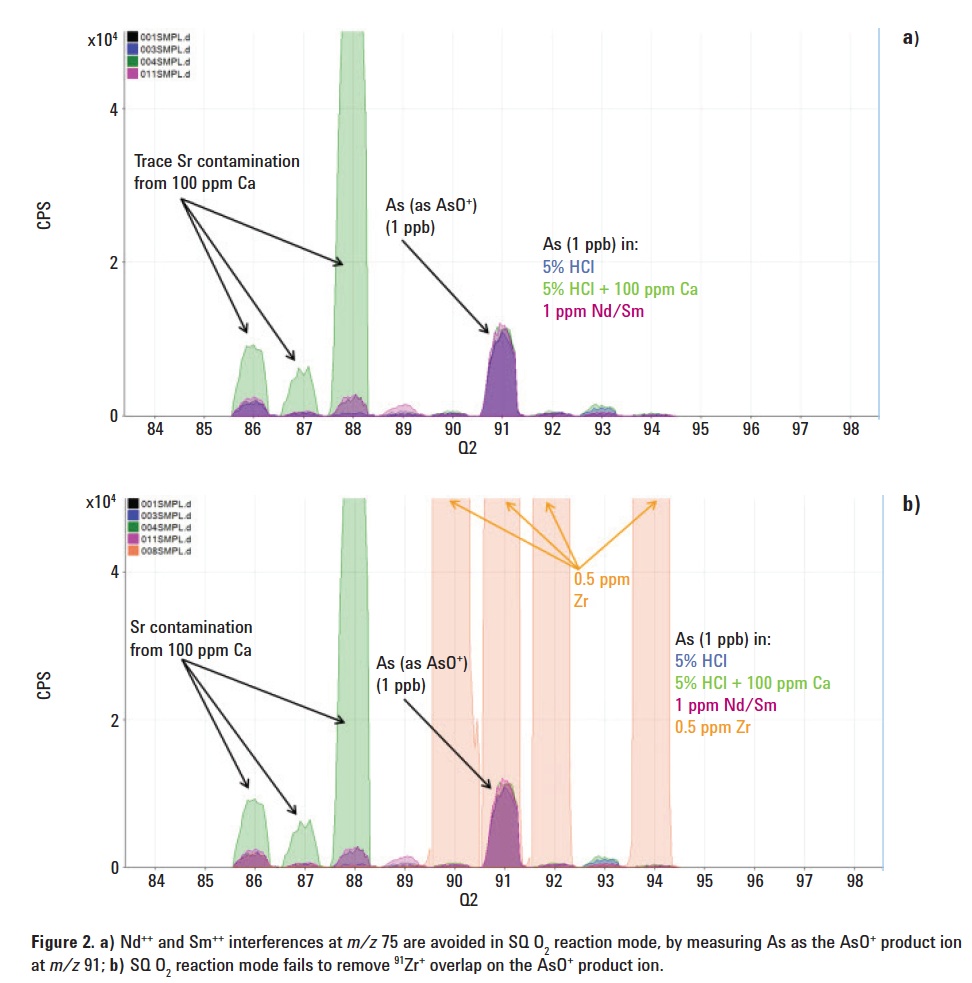
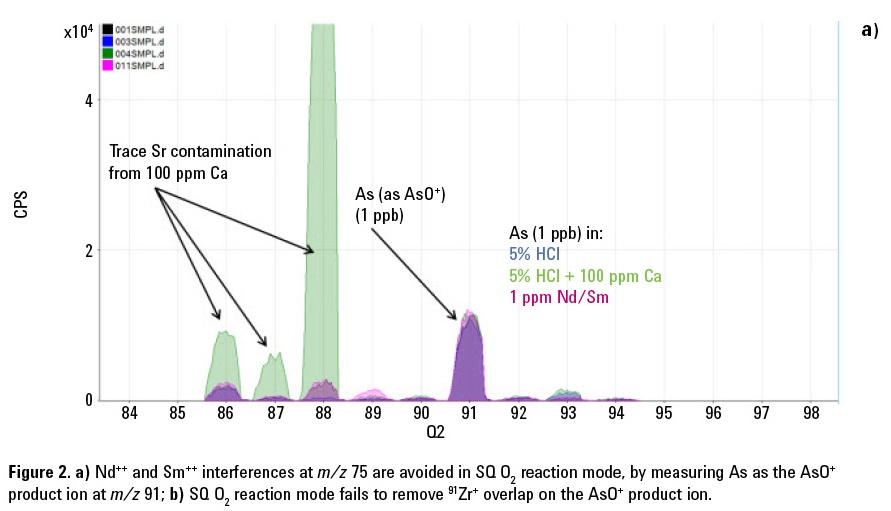
Oxygen reaction mode (O2 mode) offers a solution to these doubly-charged ion overlaps, since As can be converted to a reaction product ion 75As16O+, measured at m/z 91, where it is separated from the doubly charged Nd and Sm, which do not form such product ions. However, the new mass of the AsO+ product ion is also overlapped by an isotope of zirconium (91Zr+). The presence of Zr in a sample may therefore cause an error in the results for As measured as AsO+ using O2 reaction mode on ICP-QMS.
ICP-QQQ solves this problem, as MS/MS mode allows all masses apart from m/z 75 (including the 91Zr+ ions) to be rejected by the first quadrupole (Q1), ensuring that the AsO+ product ions can be measured free from overlap. ICP-QQQ with MS/MS therefore allows the accurate determination of As in complex samples that contain any combination of Cl, Ca, Nd, Sm and Zr.
Experimental
Reagents and sample preparation: All of the sample matrices used for this work were prepared using single-element stock solutions (Spex CertiPrep, Claritas grade). The acid matrix and elemental standard concentrations are shown in the caption for each spectrum and are representative of the acid matrix (dilute HNO3/HCl) and matrix levels commonly found in ICP-MS samples.
The sample matrices investigated were:
- Dilute nitric acid (1% HNO3)
- Dilute hydrochloric acid (5% HCl)
- Calcium (100 ppm)
- Neodymium and samarium
(1 ppm each element) - Zirconium (0.5 ppm)
Instrumentation: Agilent 8800 #100.
Plasma conditions and ion lens tune: Preset plasma/ General purpose,
Soft extraction tune: Extract 1 = 0 V,
Extract 2 = -170 V.
Acquisition conditions: Four operational modes were used, to investigate the different interference removal performance provided by the different cell modes:
- Single Quad (SQ); no gas
- Single Quad (SQ); collision mode
(using helium (He) cell gas at a flow rate of 4 mL/min) - Single Quad (SQ); reaction mode
(using oxygen (O2) cell gas at a flow rate of 0.2 mL/min). - MS/MS; reaction mode (using O2 cell gas at a flow rate of 0.2 mL/min)
KED bias voltage was +5 V in no gas and He mode, and -8 V in O2 mode.
The three “Single Quad” modes represent the performance available on conventional ICP-QMS operating in collision or reaction mode. MS/MS mode is unique to the tandem mass spectrometer configuration of the 8800 ICP-QQQ.
Results and discussion
Figures 1a, 1b and 1c illustrate how Single Quad mode with He cell gas is effective at removing the common ArCl+ and CaCl+ polyatomic interferences on As+ at m/z 75, but is ineffective against the Nd++/Sm++ interferences.
Figures 2a and 2b show how Single Quad mode with O2 reaction gas successfully avoids the doubly-charged Nd and Sm interferences by mass-shifting the As to the new AsO+ product ion mass at m/z 91; but O2 reaction mode on ICP-QMS cannot remove the 91Zr+ overlap on the AsO+ product ion.
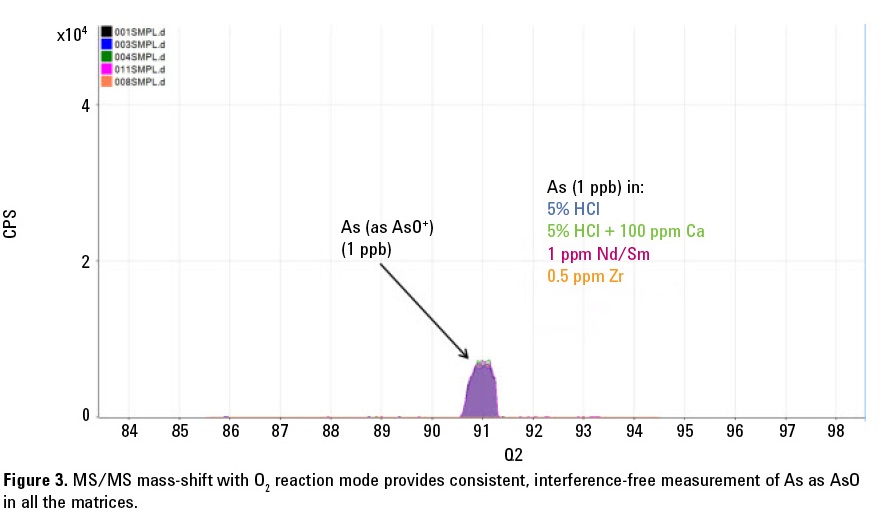
Figure 3 shows that the 8800 ICP-QQQ in MS/MS mode with O2 reaction gas provides reliable and consistent measurement of As (as AsO+) in all matrices. All the original polyatomic and doubly-charged interferences at m/z 75 are avoided by mass-shifting the As to m/z 91; and in MS/MS mode the 91Zr+ ion is removed by Q1, so the potential overlap on the AsO+ production at m/z 91 is also removed.
Conclusions
With the combination of O2 reaction mode and MS/MS operation, the 8800 ICP-QQQ provides a reliable approach to the accurate measurement of As in complex samples. All the polyatomic and doubly-charged interferences that affect As measurement at its native mass (m/z 75) are avoided by using O2 mode to mass-shift the As to its AsO+ production, measured at m/z 91. Furthermore, uniquely to the 8800 ICP-QQQ, MS/MS mode also eliminates potential native ion overlaps at m/z 91, as they are rejected by Q1 that is set to m/z 75 when measuring As.