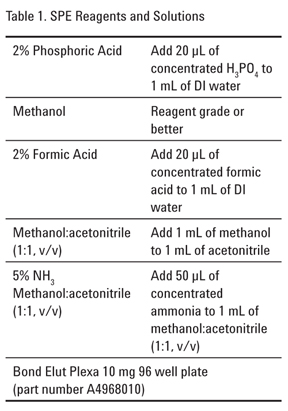
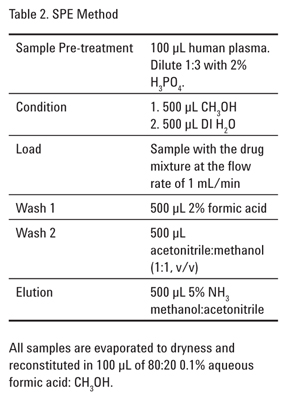
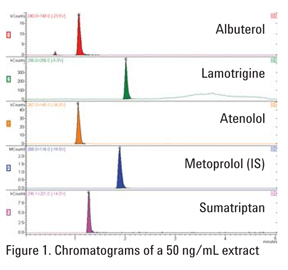
Extraction of Polar Basic Drugs from Plasma with Polymeric SPE Cation Exchange, Bond Elut Plexa PCX
William Hudson and
Andrea Junker-Buchheit
Agilent Technologies, Inc.
Application Note
BioPharma
Introduction
Basic pharmaceutical drugs are ideal for a cation exchange sorbent. Analytes are easily charged in an acidic solution and readily interact with the ion exchange function of the sorbent. Polar basic compounds can be problematic for reversed phase sorbents due to their poor hydrophobic interaction and water solubility.
Agilent Bond Elut Plexa PCX is a new addition to the Plexa family and uses a polymeric cation exchange technique. Plexa PCX uses a generic and simplified method to remove neutral and acidic interferences from the matrix and concentrate basic analytes, resulting in improved analytical performance and sensitivity in the quantification of basic compounds.
In addition, Plexa PCX offers faster and highly reproducible flow rates, resulting in excellent tube-to-tube and well-to-well performance. Plexa PCX significantly reduces ion suppression because its highly polar, hydroxylated surface is entirely amide-free. The particle exterior minimizes strong binding of proteins and phospholipids. Efficient removal of phospholipids from plasma is ensured. A simple generic method was developed for the extraction of polar basic drugs in human plasma.
Materials and Methods
Results and Discussion
LC Conditions
Mobile Phase:
A: 0.1% Formic acid
B: Methanol
Gradient:
t = 0 min 80% A : 0% B
t = 0-2 min 20% A : 80% B
t = 3.5-5 min 80% A : 20% B
Column:
Agilent Pursuit C18 3 µm,
2.0 × 50 mm
(part number A3051050X020)
MS Conditions
Transition ions and collision energy were:
Compound
Q1
Q3
CE
Albuterol
240.1
148.0
-23.5V
Lamotrigine
256.0
256.0
-5.0V
Atenolol
267.0
145.0
-34.0V
Sumatriptan
296.1
201.1
-14.0V
Capillary = 25 V, Dry gas temp = 400 °C, 30 psi, CID = Argon
Polarity: Positive
This LC/MS method describes the quantitative determination of polar basic compounds in human plasma using Bond Elut Plexa PCX for SPE (Figure 1). The limit of detection (LOD) of the solid phase extraction and LC/MS/MS analysis was
1.0 ng/mL. Recoveries were calculated from a 2nd order regression with RSD values based on a sampling of n = 6.
Excellent recoveries were achieved, which demonstrated good retention and elution, as well as minimal ion suppression. Response for all the compounds evaluated was linear up to 3 orders of magnitude from 1.0 ng/mL to 1.0 µg/mL with correlation coefficients all above 0.999. To demonstrate reproducibility, samples were analyzed at two different concentrations (n = 6). As shown in Table 3, reproducibly high recoveries were obtained according to the generic standard protocol.
Conclusions
With Agilent Bond Elut Plexa PCX, a generic drug extraction protocol from plasma can be applied to polar analytes with basic amino functional groups. Under acidic conditions, the charged analyte binds to the cation exchange groups of the sorbent (see Table 3 for pKa). Polar interferences and proteins are washed away with an acidic, aqueous solution. A neutral wash with relatively strong solvents, such as 50% methanol:acetonitrile, is possible without any loss of analyte. The wash elutes neutral compounds retained in the hydrophobic cores of the sorbent. Finally, a mixture of organic solvents with ammonia is used to disrupt the cation exchange interaction, resulting in the elution of the basic drugs.
Flow rate all over the 96-well plate is fast because Plexa PCX particles have a much narrower particle size distribution with no fines to cause blockages, thus resulting in excellent well-to-well reproducibility. Automated 96‑well technology is easily possible, which opens up new opportunities to maximize efficiency. Bond Elut Plexa PCX is therefore a useful tool for high throughput SPE applications, which require analysis at low analyte levels, validated reproducibility and quick implementation, with minimal method development. It is therefore highly recommended for bioanalytical work in pharmaceutical clinical trials, including contract research.
©Agilent Technologies, Inc., 2012
September 6, 2012
View this Application Note in its entirety: SI-01015