Extraction of Basic Drugs from Plasma with Polymeric SPE
William Hudson, David Jones,
Arnie Aistars, and Max Erwine
Agilent Technologies, Inc.
5301 Stevens Creek Boulevard
Santa Clara, CA 95051
USA
Application Note
Pharmaceuticals
Introduction
Bioanalytical solid phase extraction (SPE) has been dominated by polymeric sorbents in recent years. The ease-of-use, good flow, and resistance to effects of drying relative to silica-based sorbents make polymeric sorbents an obvious choice for high volume, high throughput assays requiring quick validation and minimal method development.
Because the method validation process is time consuming and requires high quality data, SPE methods that are fast, yet produce good recoveries with high reproducibility, are desirable. To the extent that the SPE process is streamlined without compromising data integrity, method validation can be simplified and shortened. Bond Elut Plexa minimizes method development with simple and effective methods and improves analytical sensitivity and reproducibility with an advanced polymeric structure that minimizes binding of large biomolecules to the surface, with the end result of simplifying and streamlining the SPE process.
Materials and Methods
SPE reagents and solutions
2% ammonium hydroxide
Add 20 µL concentrated ammonium hydroxide to 1 mL DI H2O
Methanol
Reagent grade or better
5% methanol
Add 5 mL methanol to 95 mL DI H2O
Bond Elut Plexa
10 mg 96 well plate (p/n A4969010)
SPE method
Sample
100 µL human plasma
Pretreat
Dilute with 300 µL 2% NH4OH
Condition
- 500 µL CH3OH
- 500 µL H2O
Wash
500 µL 5% CH3OH in H2O
Elute
500 µL CH3OH
All samples evaporated to dryness and reconstituted in 100 µL of 80:20 0.1% formic acid: CH3OH aq.
LC/MS performed – ESI, drying gas @
400 °C, 30 psi
LC conditions
Mobile phase
A
0.1% Formic acid
B
Methanol
LC gradient program
Time (min) %B
0:00 40
0:15 40
1:00 80
3:00 80
4:30 40
Column
Type
Pursuit XRs C18 3 µm, 50 × 2.0 mm
(p/n A3001050X020)
Flow rate
0.2 mL/min
Results and Discussion
The procedure described provides a simple and effective SPE method for the extraction of basic or neutral drugs from human plasma. The Limit of Quantitation (LOQ) of the combined SPE and LC/MS/MS analysis was 1.0 ng/mL. The internal standard for the application was 50 ng/mL quetiapine.
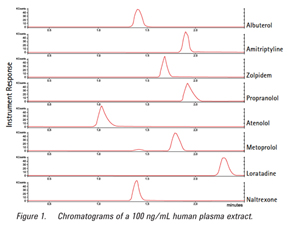
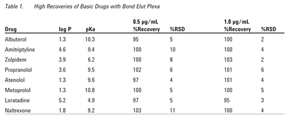
Recoveries were calculated from a second order regression with RSD values based on a sampling of n = 6. Excellent recoveries were achieved demonstrating good retention and elution, as well as minimal ion suppression. Response for all the compounds evaluated was linear up to three orders of magnitude from 1.0 ng/mL to 1.0 µg/mL with correlation coefficients all above 0.995 (n = 6). To demonstrate reproducibility, samples were analyzed at two concentrations (n = 6). Figure 1 shows the chromatograms of the extractions at 100 ng/mL. As shown in Table 1, the extractions produced reproducibly high recoveries.
Conclusions
Bond Elut Plexa is a useful tool for high-throughput SPE applications that require analysis at low analyte levels, need validated reproducibility, and must be quickly implemented with minimal method development. A single method for basic analytes covers a broad range of analyte polarites and delivers reproducibly high recoveries. Bond Elut Plexa is therefore highly recommended for bioanalytical work in pharmaceutical clinical trials, including contract research.
These data represent typical results. For more information on our products and services, visit our Web site at www.agilent.com.
©Agilent Technologies, Inc., 2011
March 21, 2011
View this Application Note in its entirety: 5990-7685EN