Removal of REE++ interference on arsenic and selenium





Kazumi Nakano and
Yasuyuki Shikamori
Agilent Technologies, Japan
Keywords
Rare Earth Elements, REE, arsenic, selenium, environmental, food, CRMs, oxygen mass-shift
Introduction
Trace analysis of arsenic (As) and selenium (Se) in environmental and food samples is of a great interest, since both elements can be toxic even at quite low levels. It is difficult to quantify As and Se accurately at trace levels in some matrices by quadrupole ICP-MS as all the analytically useful isotopes can suffer from multiple spectral interferences, as summarized in Table 1. This application investigates ICP-QQQ in MS/MS reaction mode to remove interferences on As and Se, with an emphasis on the removal of the doubly-charged ions arising from Rare Earth Elements (REE++). While the concentration of REEs in environmental and food samples is usually low, some plants will accumulate REEs from the soil, and a high concentration will lead to false positive results for As and Se.
Experimental
Instrumentation: Agilent 8800 #100.
Plasma conditions: Preset plasma/Low matrix.
Ion lens tune: Soft extraction tune:
Extract 1 = 0 V, Extract 2 = -180 V.
CRC conditions: O2 gas flow rate of
0.2 mL/min, Octopole bias = -8 V and
KED = -6 V.
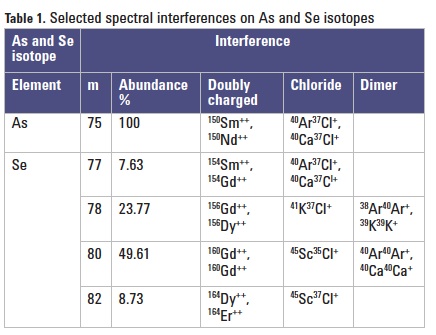
Acquisition parameters: MS/MS O2 mass-shift method to measure As+ (as AsO+) and Se+ (as SeO+), as illustrated in Figure 1. Unlike conventional quadrupole ICP-MS, the 8800 ICP-QQQ mass-shift method can be applied to complex matrix samples that may contain Zr and/or Mo. The MS/MS configuration prevents undesired ions such as 91Zr+ and 94Mo+ from overlapping the MO+ product ions, as they are rejected by Q1.
Samples and sample preparation: SPEX XSTC-1 (a mixture of 10 ppm each of Ce, Dy, Er, Eu, Gd, Ho, La, Lu, Nd, Pr, Sm, Sc, Tb, Tm, Yb and Y) purchased from SPEX CertiPrep Ltd. (UK) was used. Four certified reference materials (CRMs): NIST 1515 Apple Leaves, NIST 1573a Tomato Leaves, NIST 1575a Pine Needles and NMIJ 7531a Brown Rice, were used for the method validation. It should be noted that NIST 1515 contains 3 mg/kg Sm and Gd, and 0.2 mg/kg Eu. NIST 1573a contains 0.19 mg/kg Sm, 0.17 mg/kg Gd, 5% Ca and 2.7% K, a combination of matrix elements that might be expected to cause severe interferences on As and Se. All CRMs were microwave-digested in HNO3 and H2O2, diluted and analyzed.
Results and discussion
Effectiveness of O2 mass-shift method for removing REE++ interferences
To investigate the effectiveness of interference removal modes on the 8800 ICP-QQQ, As and Se were measured in a mixed REE solution containing 1 ppm each of Ce, Dy, Er, Eu, Gd, Ho, La, Lu, Nd, Pr, Sm, Sc, Tb, Tm, Yb and Y.
Three different 8800 ICP-QQQ cell modes were used:
- Single Quad (SQ); no gas
- Single Quad (SQ); reaction mode using hydrogen (H2) cell gas
- MS/MS; reaction mode using O2 cell gas with + 16amu mass-shift
"Single Quad” represents the performance of conventional ICP-QMS while MS/MS mode is unique to ICP-QQQ.
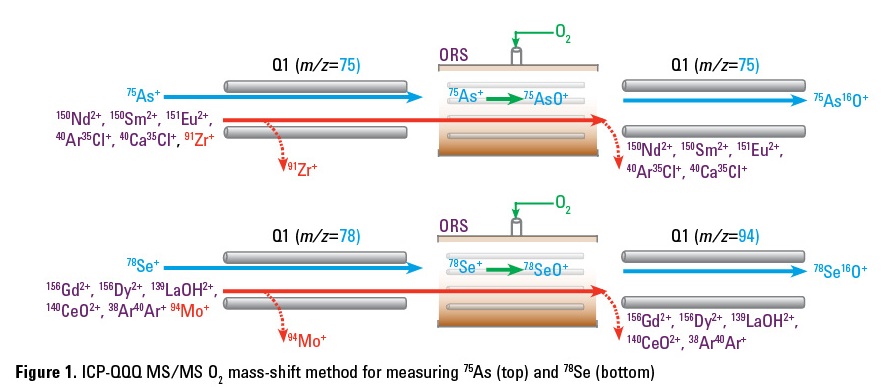
Figure 2 shows the BECs of As and Se in each of the measurement modes. The results in Figure 2 illustrate the excellent interference removal performance of the
O2 mass-shift method for the detection of
As and Se in a matrix containing REEs.
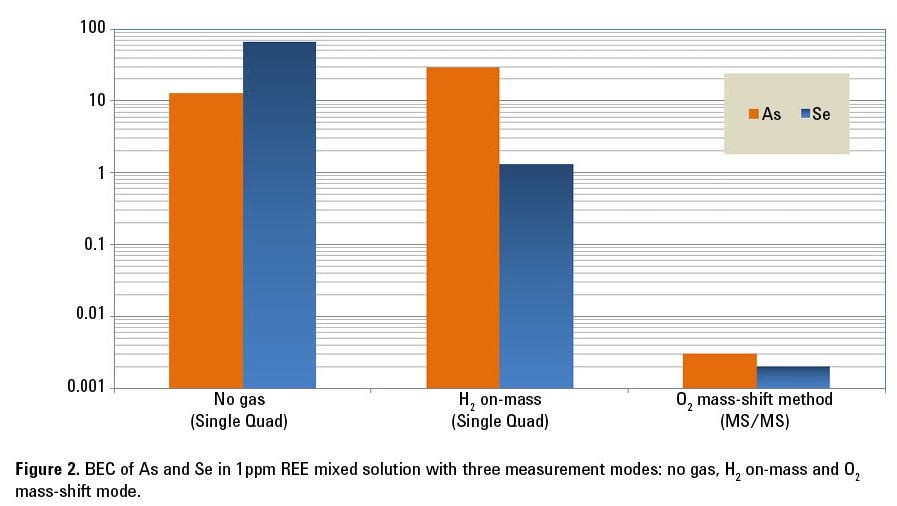
Figure 3 shows the product ion scan spectra obtained using O2 mass-shift mode for a solution containing 1 ppm REEs without (left) and with (right) a 1 ppb As spike. As illustrated in the schematic,
Q1 was fixed at m/z = 75 and Q2 was scanned across the selected mass range, to monitor all existing and cell-formed ions derived from precursor ions at m/z 75. Figure 3 (left) shows the product ions from
m/z 75 in the blank REE matrix; the signal at Q2 m/z = 75 (mass of As) is due to REE++. The absence of a signal at m/z = 91 (the mass of AsO+) in the blank REE matrix, indicates that the REEs do not react with O2 in the cell to give rise to product ions (such as REEO2++) that overlap AsO+ at m/z 91. Consequently, As can be successfully measured as AsO+ at m/z = 91 as shown in Figure 3 (right).
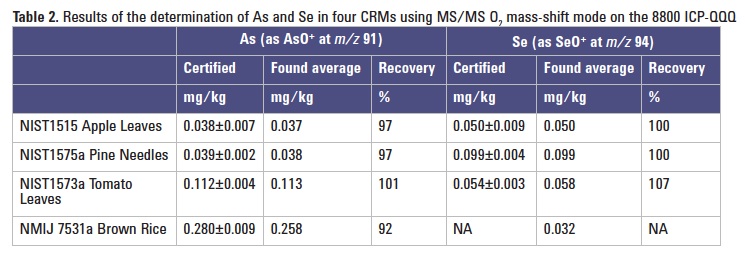
Method validation with CRMs
The ICP-QQQ method was applied to the measurement of As and Se in four CRMs. Table 2 summarizes the results. The measured concentrations of As and Se in the CRMs were all in good agreement with the certified values.