Silicon wafer analysis by ICP-QQQ: Determination of phosphorus and titanium in a high silicon matrix





Junichi Takahashi
Agilent Technologies, Japan
Keywords
semiconductor, silicon wafer, phosphorus, titanium, Vapor Phase Decomposition, VPD, oxygen mass-shift
Introduction
The semiconductor industry first used
ICP-MS for trace element analysis in the early 1980s. Nowadays the technique is widely used for control of trace impurities in materials and chemicals, particularly by silicon device manufacturers. The major challenge for quadrupole ICP-MS
(ICP-QMS) is the presence of spectroscopic interferences on key contaminant elements, although performance has been gradually improved through developments such as cool plasma and collision/reaction cells (CRC), and improved performance has also been provided by high resolution ICP-MS. Consequently metallic impurity control of silicon wafers can be successfully monitored by ICP-MS in the case of low silicon samples such as Vapor Phase Decomposition (VPD) of native silicon wafers. However, difficulties of Si-based spectral interferences, particularly on P and Ti, still affect the analysis of samples that contain high concentrations of Si, such as VPD samples of thermally oxidized wafers and samples relating to bulk silicon wafers. These interferences cannot be reduced adequately by ICP-QMS and have required HR-ICP-MS. In this paper, we evaluate triple quadrupole ICP-MS with MS/MS technology for the determination of ultratrace P and Ti in a high Si matrix.
Experimental
Instrumentation: Agilent 8800 #200 with an inert sample introduction kit including a low flow nebulizer (PFA-20) and a Pt/Ni skimmer cone. The actual sample uptake rate was 36 μL/min. The sample was self-aspirated from an Agilent I-AS autosampler.
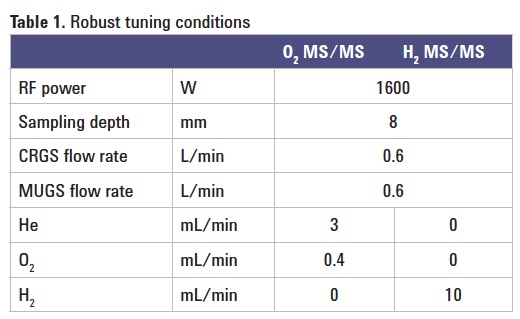
Plasma conditions: Robust tuning conditions were applied as summarized in Table 1.
Ion lens tune: Extract 1 = 0 V was used and other lens voltages were optimized using Auto tune.
Sample preparation: Silicon wafer samples were dissolved in TAMAPURE HF/HNO3 and the final Si concentration was adjusted to 2000 ppm.
Results and discussion
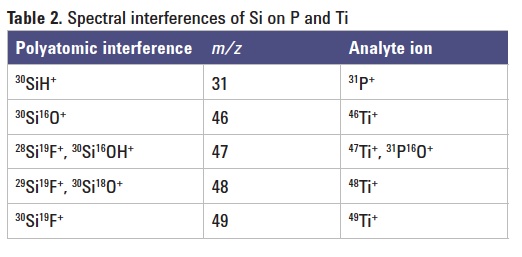
Phosphorus is monoisotopic at m/z 31, and suffers an interference from 30SiH. While P+ can be detected as PO+ under cool plasma conditions, it is difficult to maintain cool plasma when the matrix concentration is high. Si sample solutions always contain HF, so Si will form SiF (IP: 7.54 eV) that also interferes with Ti. Table 2 shows the Si-based spectral interferences on P and Ti. Using the 8800 ICP-QQQ operating in MS/MS mode with O2 mass-shift, P and Ti can be determined as their oxide ions, avoiding the Si-based interferences.
For Ti analysis, Q1 is set to m/z 48, and so will transmit 48Ti+ and any other interfering ions at mass 48, such as 29Si19F+ and 30Si18O+. But only 48Ti reacts with oxygen in the CRC, producing the product ion 48Ti16O+, which is transmitted by setting Q2 to m/z 64. NH3 can be used as an alternative reaction gas, as it produces 48Ti14NH+ that can be detected at m/z 63.
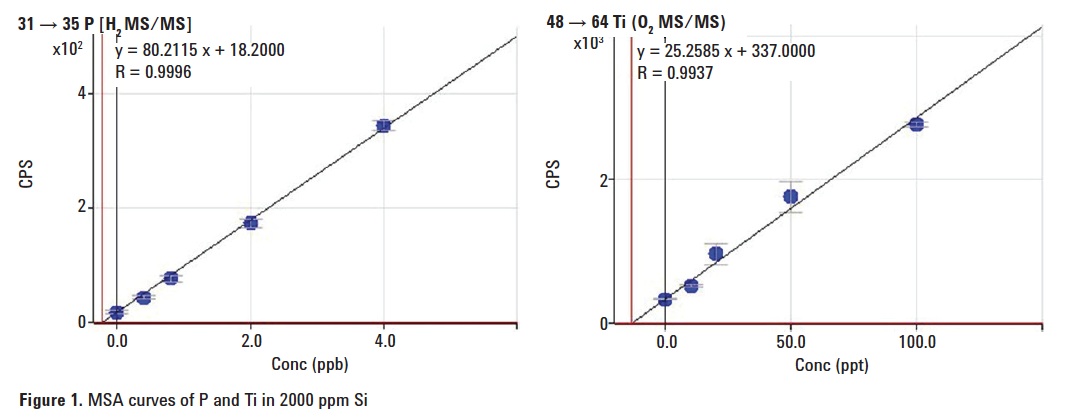
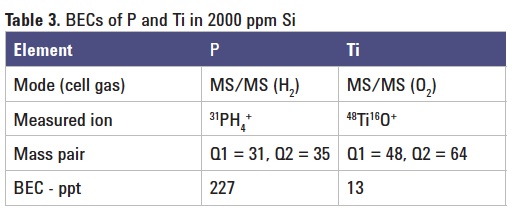
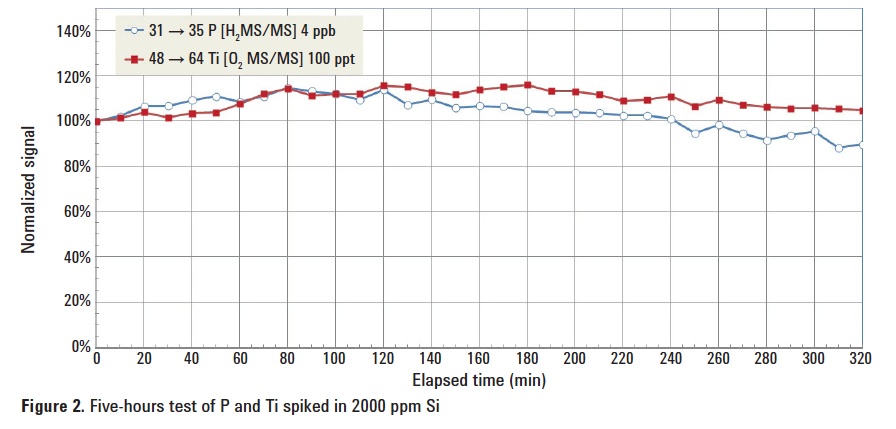
31P+ reacts readily with O2 to form 31P16O+. The selection of ions at m/z 31 by Q1 eliminates the spectral interference of 28Si19F. However, 30SiH passes through Q1 and reacts with O2 to create 30Si16OH. In order to determine P in a high Si matrix, H2 mass-shift is a preferred option, despite the relatively low efficiency of production of PH3+ or PH4+ ions. The MSA calibration curves for P and Ti in a matrix of 2000 ppm Si are shown in Figure 1. The calculated BECs are summarized in Table 3. A long term stability test was carried out by analyzing a spiked sample repeatedly over five hours (Figure 2).
Conclusions
The MS/MS mass-shift mode of the ICP-QQQ is effective for the determination of P, Ti and other trace elements in high purity silicon matrices, providing effective removal of the potential Si-based polyatomic interferences.
More information
Improvement of ICP-MS detectability of phosphorus and titanium in high purity silicon samples using the Agilent 8800 Triple Quadrupole ICP-MS, Agilent application note, 5991-2466EN.