Measurement of selenium in clinical samples in the presence of gadolinium-based magnetic resonance imaging contrasting agents



Glenn Woods
Agilent Technologies (UK) Ltd.
Keywords
selenium, enzyme, blood, serum, urine, MRI contrasting agents, gadolinium, molybdenum, zirconium, neutral gain scan, oxygen mass-shift
Introduction
Selenium is an important micronutrient for human, mammalian, bacterial and plant life and is contained within several co-factors and enzyme systems. It is monitored in blood, serum and urine as part of human health, and a deficiency can indicate an illness (particularly if the levels change suddenly), such as cancer, diabetes and tuberculosis (TB).
For cancer patients, determining the location of the tumour often requires the use of Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). However, for some soft tissues such as the brain, a “contrasting agent” is needed to effectively show the location of the tumour or problem area. There are several contrasting agents which are salts or chelates of gadolinium (III) (Gd(III)), trade names are given in brackets:
Gadodiamide (Omniscan), Gadobenate (MultiHance), Gadopentetate (Magnevist), Gadoteridol (ProHance), Gadofosveset (Ablavar, formerly Vasovist), Gadoversetamide (OptiMARK), Gadoxetate (Eovist), Gadobutrol (Gadavist)
Unfortunately Gd has a relatively low second ionization potential (12.09 eV) meaning it can form Gd++ ions in the plasma. These Gd++ ions appear at half their original mass (as a quadrupole measures ions based on their mass to charge ratio or m/z) and form interferences on all of the main analytical isotopes of Se. This is complicated to a greater extent as Gd has several odd-mass isotopes which form Gd++ interferences at half-mass (e.g., 155Gd++ would appear at m/z 77.5). This makes the spectrum in the mass region of the Se isotopes quite complex when Gd is present in the sample. In a typical patient's sample, the Gd concentration can vary between zero to several thousand parts per billion (µg/L). Because of the variability from patient-to-patient (which is also time-dependant on a sample-to-sample basis due to the contrasting agent’s half-life in the body) a simple mathematical correction cannot always be made or a constant “background” be assumed.
Experimental
In order to remove the Gd-based interference, Se+ can be reacted with oxygen cell gas in the collision/reaction cell to produce SeO+ as a product ion. The
Se-O reaction is slightly endothermic
(ΔHr = 0.71 eV) which means that the reaction yield for SeO+ would be relatively low. However the bias voltage on the ORS can be adjusted to increase the ion energy improving reaction yield significantly over a more “thermalized” approach. These conditions are referred to as high ORS bias conditions.
Instrumentation: Agilent 8800 #100.
Plasma conditions: Preset plasma/General purpose.
Ion lens tune: Soft extraction tune: Extract 1 = 0 V, Extract 2 = -170 V.
CRC conditions: O2 gas at 0.3 mL/min,
Octopole bias = -15 V, KED = -8 V.
Results and discussion
O2 mass-shift method
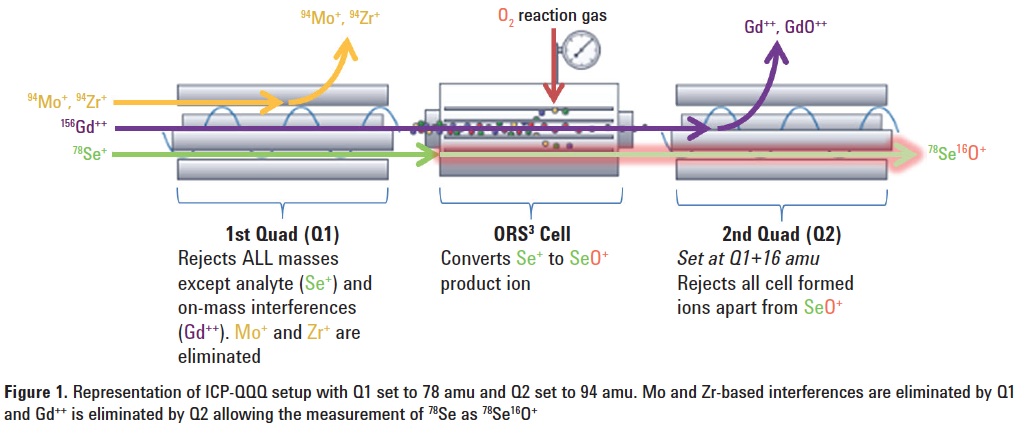
Using O2 mass-shift, the analyte is measured at M +16 amu (e.g. 78Se+ is measured as 78Se16O+ at 94 amu). With conventional quadrupole ICP-MS, any 94Mo or 94Zr present in the sample would interfere with the measurement at this mass. However, with MS/MS mode, 94Mo or 94Zr are removed by Q1 as it is set to the mass of the Se+ precursor ion at 78 amu, and 156Gd++ is eliminated as Q2 is set to the SeO+ product ion mass of 94 amu. Even if Gd did form GdO++ this would also be eliminated by Q2 as the apparent mass (m/z) of 156Gd16O++ is 172/2 (86 amu). Figure 1 is a graphical representation of the MS/MS setup.
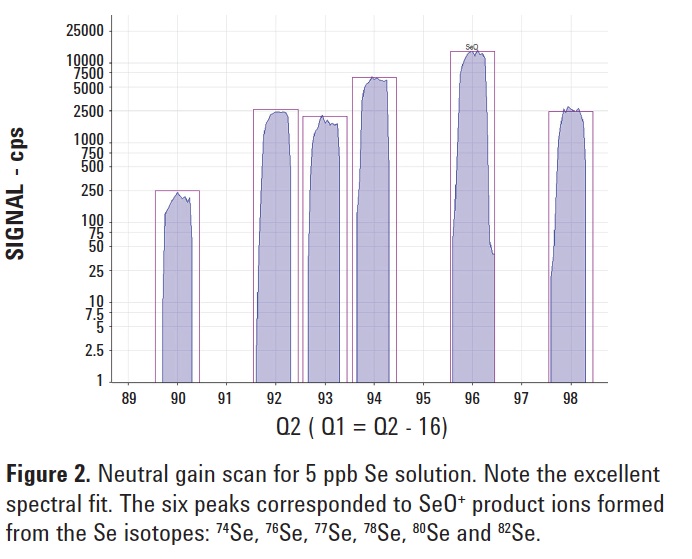
To check for efficient conversion of Se+ to SeO+, a neutral gain scan covering the mass range of all the SeO+ product ions was performed for a 5 ppb Se solution. Figure 2 displays the isotope pattern of the + 16O-atom transitions for all the
Se isotopes, showing a perfect match with the theoretical isotopic fit.
Se measurement in human serum
Instrument cell conditions were optimized using a Se standard in a simple
HNO3 matrix. A pooled human serum sample was prepared by 10x dilution into a basic diluent consisting of
NH4OH (0.5%), H4-EDTA (0.01%),
BuOH (2%) & Triton X-100 (0.01%) in ultrapure water. The sample was prepared unspiked and also spiked with
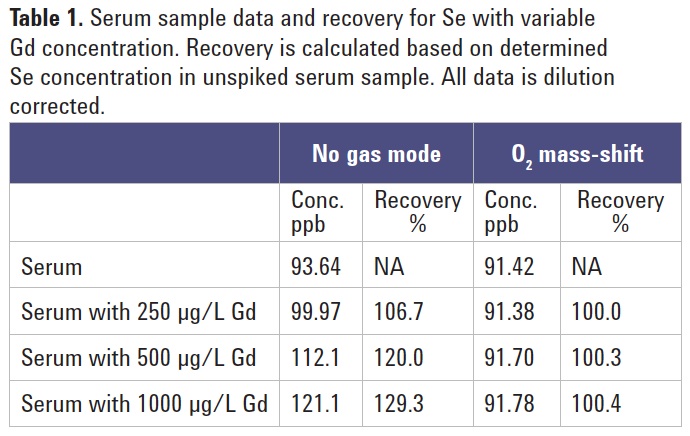
Gd equivalent to 250, 500 and 1000 µg/L in the original sample, and analyzed using the 8800 ICP-QQQ in no gas and O2 mass-shift modes of operation for comparison. The data is summarized in Table 1. The results show that, under no gas conditions, the apparent Se concentration is influenced by the variable Gd++ interference. Recovery based upon the original unspiked sample demonstrates an over-recovery of almost 130% for the no gas data when Gd is at a concentration of 1000 µg/L. In contrast, the Se data measured with MS/MS mass-shift mode remains essentially constant at all levels of Gd matrix. This would indicate that the O2 mass-shift reaction is independent of the Gd concentration and is highly applicable to this relatively difficult and important application.